Introduction to GSC Fast Flowering Strain
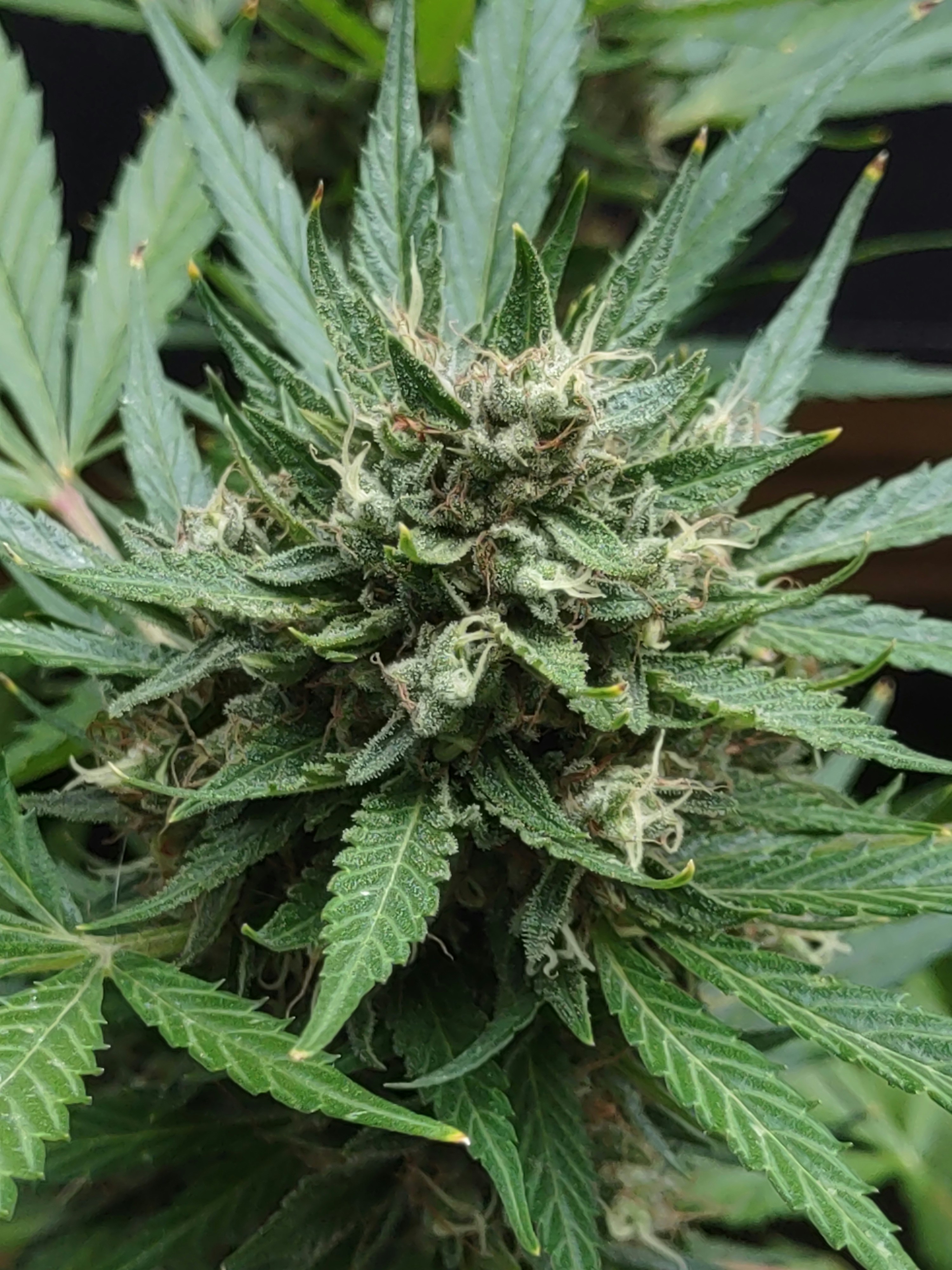
The GSC Fast Flowering Strain, commonly referred to as Girl Scout Cookies, has become increasingly popular among cannabis growers due to its remarkable characteristics. Renowned for its outstanding yield and potent effects, this strain stands out in the world of cannabis cultivation. It is the result of a genetic combination of the original Girl Scout Cookies and various other cultivars, specifically bred to exhibit a faster flowering period. This breeding process enhances the strain’s appeal by enabling growers to achieve quicker harvests without compromising on quality.
GSC fast flowering strain showcases a unique blend of flavors and aromas, making it favorable among users who appreciate both its therapeutic and recreational benefits. The strain is characterized by its sweet and earthy notes, harmonized with hints of mint and chocolate, reminiscent of the beloved cookies it’s named after. Notably, the compact and dense buds produced by this strain boast high resin production, making them ideal for extraction processes and ensuring a potent smoking experience.
As the cannabis market continues to evolve, the demand for fast flowering strains like GSC has grown significantly. This inclination is attributed to the time-sensitive nature of cultivation; growers often seek strains that reduce the waiting period while still delivering a high-quality product. Compared to traditional strains that may take longer to bloom, the GSC Fast Flowering Strain allows for a quicker turnaround, which increases profitability and provides an opportunity for multiple harvests within a growing season. This remarkable efficiency, combined with its robust effects, positions the GSC fast flowering strain as a versatile option for both novice and experienced cultivators alike.
Understanding the Growth Cycle of GSC
The growth cycle of the GSC (Girl Scout Cookies) fast flowering strain can be characterized by two primary phases: the vegetative stage and the flowering stage. Understanding these stages is crucial for any cultivator seeking to optimize their yields and enhance the quality of their harvest. Effective management of these stages requires attention to light cycles, nutrients, and environmental conditions.
During the vegetative stage, which typically lasts for 4 to 6 weeks, the GSC strain focuses on developing a robust structure. This phase is pivotal as it sets the foundation for future growth. For indoor cultivators, maintaining a light cycle of 18 hours of light and 6 hours of darkness encourages vigorous growth. It is essential to provide adequate nutrients during this phase, including nitrogen, to support leaf development and overall plant health. Ensuring proper airflow and humidity levels is also critical, as too much moisture can lead to mold or pests that can harm the plants.
Transitioning into the flowering stage, this strain generally begins around week 6 when the light cycle is altered to 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness. This change signals the plants to develop buds. During this period, it is important to manage environmental factors meticulously, as humidity levels and temperatures can greatly impact flowering. Maintaining lower humidity levels while providing sufficient phosphorus and potassium can significantly enhance bud density and quality. Throughout this phase, monitoring the plants for any signs of nutrient deficiency or overwatering will ensure a healthy flowering process.
The harmonious relationship between light management, nutrient provision, and environmental control is fundamental for growing the GSC fast flowering strain successfully. By understanding each stage in this growth cycle, cultivators can strategically implement practices that heighten the plant’s resilience and productivity, ultimately achieving a successful harvest.
Optimal Growing Conditions for GSC
Growing the GSC fast flowering strain successfully requires an understanding of its optimal growing conditions, which are crucial for achieving vigorous growth and maximizing yield. One of the primary factors to consider is temperature. Generally, GSC thrives best in a temperature range of 70°F to 80°F (20°C to 27°C) during the day, while nighttime temperatures can drop slightly. Maintaining consistent temperatures within this range helps to prevent stress on the plants, which can adversely affect growth and flowering.
Humidity levels are also essential. During the vegetative phase, a humidity level of 40% to 70% can encourage lush growth, but as the plants transition into the flowering stage, it is advisable to reduce humidity to around 40% to 50%. This decrease helps to prevent mold and mildew, which can be detrimental to the GSC flowers. Implementing proper ventilation and dehumidifiers can assist in maintaining the desired humidity levels.
Soil composition is another critical aspect that influences the growth of GSC fast flowering strains. A well-draining soil rich in organic matter is ideal, as it provides the necessary nutrients while allowing for adequate aeration. Adding compost or high-quality potting mix can greatly enhance soil fertility. Additionally, incorporating perlite or vermiculite can improve drainage, further promoting healthy root development.
In terms of light requirements, the GSC strain flourishes under full-spectrum light. During the vegetative stage, a light cycle of 18 hours on and 6 hours off should be maintained, transitioning to a 12/12 cycle during flowering. Utilizing high-intensity discharge (HID) lights or LED grow lights can significantly increase photosynthesis, leading to faster growth and a more bountiful harvest. By carefully managing these optimal growing conditions, cultivators can learn how to grow GSC fast flowering strain with remarkable efficiency.
Nurturing Nutrient Needs for Rapid Growth
Successfully cultivating the GSC fast flowering strain requires a deep understanding of its nutrient needs throughout various stages of growth. Each phase, from seedling to flowering, has its own distinct requirements that must be met to promote healthy development and optimize growth efficiency. By providing the right soil amendments, fertilizers, and enhancements, growers can not only ensure robust plants but also significantly reduce the flowering period.
In the initial seedling stage, plants benefit from a lighter nutrient mix to prevent over-fertilization, which can stunt growth. A soil mix rich in organic matter, such as compost, provides essential micronutrients while maintaining proper drainage. As seedlings develop their first few leaves, introducing a low-nitrogen fertilizer can support healthy growth without overwhelming the plants. Additionally, ensuring the pH of the soil remains between 6.0 and 6.5 is vital for optimal nutrient uptake.
As the plants transition into the vegetative stage, the nutrient requirements become slightly more demanding. It is beneficial to increase the nitrogen levels in the fertilizer, as this encourages lush foliage development. A balanced nutrient solution that includes phosphorus and potassium will support the overall health of the GSC fast flowering strain, ensuring strong root development in preparation for the upcoming flowering phase.
Once the flowering stage begins, the focus should shift to enhancing the phosphorus and potassium levels in the fertilization regimen. These elements are crucial for flower formation and can significantly impact the yield and quality of the harvest. Employing organic additives such as bat guano or bone meal can provide an additional nutrient boost that aligns well with the GSC strain’s growth patterns. Regularly monitoring the nutrient levels helps adjust feeding schedules accurately, ensuring the plants receive the right balance for optimal flowering performance. With tailored care and thoughtful nutrient management, growers can effectively learn how to grow GSC fast flowering strain and enjoy a successful harvest.
Techniques to Enhance Growth Speed
In order to effectively learn how to grow GSC fast flowering strain, implementing specific cultivation techniques can significantly enhance growth speed while ensuring plant health. A combination of topping, low-stress training (LST), and the Screen of Green (Scrog) method can yield impressive results in a shorter timeframe.
Topping is a technique that involves cutting off the top of the main stem, which encourages the plant to focus its energy on developing side branches. When performed at the right time, topping can promote bushier growth and create an even canopy, which is beneficial for light distribution. It is important to ensure the plant is healthy and sufficiently developed before topping, as this minimizes stress and fosters a quicker recovery.
Low-stress training (LST) is another effective method for accelerating growth. This technique involves gently bending and securing the plant’s branches to encourage horizontal growth instead of vertical. By spreading out the plant, LST improves exposure to light and facilitates better air circulation. The result is often a more robust plant that can yield more flowers when it comes time to harvest. It is crucial to monitor the plant’s response to LST; gradual adjustments will help maintain its health while promoting faster growth.
The Scrog method, or Screen of Green, is an advanced technique that requires the use of a screen or net to support the plant as it grows. This method aims to create an even canopy by weaving branches through the screen, allowing for optimal light penetration and airflow. This setup not only maximizes yields but also ensures that the plant’s energy is distributed evenly across all bud sites. Scrog can be an effective way to grow GSC fast flowering strain, especially in limited space.
By utilizing these techniques—topping, LST, and Scrog—growers can enhance the growth speed of the GSC fast flowering strain, leading to a successful harvest without compromising plant health.
Pest and Disease Management for GSC Growers
Successful cultivation of the GSC fast flowering strain requires a thorough understanding of potential pests and diseases that can compromise plant health and yield. The GSC strain is particularly sensitive to pests such as spider mites, aphids, and whiteflies, which can quickly infest a grow space if not managed effectively. Regular inspection of plants is crucial for early detection of these pests. Look for yellowing leaves, webbing, or visible insects, and take immediate action if seen.
To prevent pest infestations, growers should implement an Integrated Pest Management (IPM) approach. This includes maintaining optimal growing conditions that discourage pests, such as managing humidity levels, ensuring proper air circulation, and avoiding overcrowding of plants. Additionally, introducing beneficial insects, like ladybugs and predatory mites, can help naturally control pest populations.
Fungal diseases such as powdery mildew and root rot can also pose significant risks to GSC growers. Powdery mildew, often characterized by a white powdery substance on leaves, thrives in high humidity and poor airflow. To mitigate this risk, growers should ensure adequate spacing between plants to promote airflow and utilize fungicides as a preventive measure. Watering practices also play a critical role; watering in the morning allows the foliage to dry throughout the day, reducing fungal growth conditions.
In terms of treatment, there are various organic options available for pest and disease management. For instance, neem oil is effective against numerous pests and can act as a fungicide. Similarly, hydrogen peroxide can combat root rot by increasing oxygen availability in the soil. By being proactive in pest and disease management, GSC growers can enhance plant health significantly, leading to optimal growth and maximized yields. Understanding how to grow GSC fast flowering strain involves not only cultivation techniques but also adeptness in managing these challenges effectively.
Harvesting and Curing Techniques for GSC
Harvesting the GSC fast flowering strain requires careful attention to detail to ensure optimal quality and yield. One of the primary indicators that it is time to harvest is the trichome coloration. Growers should aim to harvest their GSC plants when approximately 70% of the trichomes have turned milky white and about 30% have turned amber. This window allows for a balanced effect between potency and flavor. Improper timing, whether too early or too late, may lead to a less desirable final product.
Another vital sign to look for is the pistil coloration. The pistils will typically change from white to a dark orange or brown hue. When about 70% of the pistils have changed color, it signals that the plant is ready for harvest. It is essential to monitor these signs regularly as they can change quickly, especially in the fast flowering GSC variety.
Once optimal harvesting time is determined, the next crucial step is curing. Curing enhances the flavor and potency of the GSC fast flowering strain, making it more enjoyable for consumers. After cutting the buds, they should be hung upside down in a cool, dark, and well-ventilated room for approximately 7 to 14 days. This drying phase is crucial as it removes excess moisture and prepares the buds for curing.
Following the drying process, buds should be placed in airtight jars, filled about three-quarters full to allow for some air while preventing excess humidity. It is advisable to open these jars daily for the first week to release any built-up moisture, a practice known as “burping.” After the first week, this can be reduced to once every few days. Proper curing can last up to four weeks or more, leading to a smoother smoke and enhanced flavor profile. Growers who implement these harvesting and curing techniques will know exactly how to grow GSC fast flowering strain to its fullest potential.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Growing GSC Fast Flowering Strain
Growing the GSC fast flowering strain can be a rewarding experience for both novice and experienced cultivators. However, several common mistakes can hinder the growth and overall quality of the plants. Awareness of these pitfalls is crucial for ensuring a successful growing experience.
One prevalent mistake is over-watering. This strain, like many others, requires a careful balance of moisture in the soil. Over-watering can lead to root rot and other related issues, stunting growth. It is essential to monitor soil moisture closely and only water when the top inch of soil feels dry. Conversely, under-watering can also be detrimental, emphasizing the need for judicious and methodical watering practices.
Nutrient management is another critical area where growers often falter. GSC fast flowering strain plants may exhibit nutrient deficiencies or toxicities if the nutrient regimen is not carefully tailored. Too many nutrients, particularly nitrogen during the flowering phase, can lead to lush foliage at the expense of bud development. Regularly testing soil and employing a balanced feed schedule will help maintain the ideal nutrient levels and promote healthy plant growth.
Additionally, lighting plays a crucial role in the successful cultivation of GSC. Many inexperienced growers may underestimate the importance of light intensity and spectrum. Insufficient or inappropriate lighting can lead to poor yields and a longer flowering phase. For optimal results, growers must employ high-quality grow lights that simulate natural sunlight and maintain an adequate light-to-dark cycle.
Lastly, neglecting pest and disease management can have severe repercussions. Regularly inspect plants for signs of pests or diseases, and take preventive measures early to avoid widespread infestations. Utilizing integrated pest management practices can greatly reduce the chance of encountering these issues.
Being aware of these common mistakes and proactively avoiding them is essential for successfully growing the GSC fast flowering strain, leading to healthy plants and bountiful harvests.
Conclusion and Final Tips for GSC Growers
In conclusion, cultivating the GSC fast flowering strain can be a rewarding experience, provided that growers adhere to best practices and remain attentive to the specific needs of the plant. This strain is known for its unique flavor profile, balanced effects, and rapid growth cycle, making it a popular choice among both novice and experienced cannabis cultivators.
To effectively grow GSC fast flowering strain, it is essential to create an optimal growing environment. This includes maintaining appropriate temperature and humidity levels while ensuring that the plants receive adequate light during both the vegetative and flowering stages. The right nutrients, tailored to the specific growth phases, will also play a crucial role in maximizing yield and quality. Regular monitoring for pests and diseases is vital, as prevention allows for healthier plants and reduces the possibility of significant crop loss.
Additionally, experimenting with various cultivation techniques, such as topping, low-stress training (LST), or using hydroponic systems, can significantly impact growth and yield. These strategies can enhance light exposure and promote better airflow, ultimately leading to a more abundant harvest. However, it is imperative that growers respect the natural growth characteristics of the GSC strain, avoiding excessive interference that could hinder its development.
Finally, patience and observation will be key throughout the growing process. Each grow may present unique challenges and learning opportunities. Adapting techniques based on personal experience and environmental conditions can help increase the effectiveness of your cultivation efforts. By following these guidelines and remaining open to experimentation, growers will find themselves well-equipped to successfully cultivate the GSC fast flowering strain, achieving satisfying results in terms of both yield and quality.