Ever wondered why raw cannabis doesn’t get you high? The answer lies in a fascinating compound called THCA. This key player in the cannabis world has been turning heads in the scientific community, but what exactly does it do in our bodies?
THCA, short for tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, is abundant in fresh cannabis plants. Unlike its famous cousin THC, THCA doesn’t produce psychoactive effects. This unique property stems from its molecular structure, which includes a carboxylic acid group. But don’t let its non-intoxicating nature fool you – THCA packs a punch when it comes to potential health benefits.
From fighting inflammation to protecting brain cells, THCA’s effects on the body are diverse and promising. Research suggests it may help with nausea, oxidative stress, and even neurodegenerative diseases. As we delve deeper into the world of THCA, we’ll uncover how this compound interacts with our bodies and why it’s becoming a hot topic in cannabis research.
Introduction to THCA
THCA cannabis is a fascinating compound that’s gaining attention in the world of wellness. As we explore THCA vs THC, it’s important to understand their unique properties and effects on the body.
What is THCA?
THCA, or tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, is a cannabinoid found in raw cannabis plants. Unlike THC, THCA doesn’t produce a “high.” It’s the precursor to THC and has a unique structure that prevents it from binding to brain receptors.
Differences Between THCA and THC
The main difference between THCA and THC is their effects and legal status. THCA is non-intoxicating and has anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties. THC, however, is psychoactive and produces a “high.”
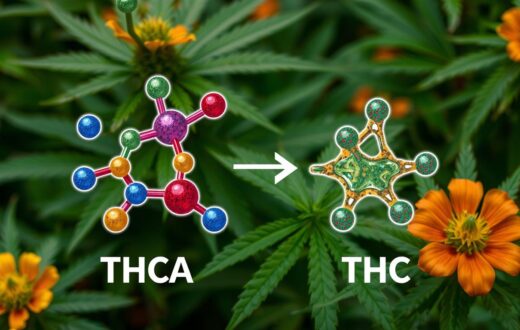
Interestingly, THCA turns into THC when cannabis is heated or exposed to light for a long time. THC is federally illegal in the US, but THCA is legal under the 2018 Farm Bill, as long as it has less than 0.3% THC. This legal difference has made THCA cannabis products more popular. They can be consumed raw, like in juices or smoothies, to potentially get health benefits without getting high.
The Chemical Structure of THCA
THCA’s chemical structure is key to understanding its role in the body. It’s the precursor to THC, a major cannabinoid in cannabis plants.
Molecular Composition
THCA’s molecular makeup is close to THC but has a big difference. It has a carboxylic acid group (COOH) in its structure. This group makes THCA unique and non-psychoactive.
Role of Carboxylic Acid
The carboxylic acid group in THCA is why it doesn’t get you high. When THCA is heated, like when smoking or cooking, it changes. This process, called decarboxylation, removes the acid group, turning THCA into THC.
This change is why raw cannabis doesn’t get you high, but heated cannabis does. Knowing about THCA’s structure helps us see why it’s safe to eat raw. Many people use raw cannabis juice or other non-heated methods. This way, they can enjoy its benefits without the high.
THCA’s Interaction with the Endocannabinoid System
THCA, found in raw cannabis, has a special connection with our body’s natural system. It doesn’t make us feel “high” like THC does. Yet, it might still offer some benefits.
Overview of the Endocannabinoid System
Our bodies have a complex network called the endocannabinoid system (ECS). It helps control mood, pain, and our immune system. The ECS uses natural compounds called endocannabinoids to do this.
This system is crucial for keeping our bodies in balance. It helps us stay healthy and feeling good.
How THCA Binds to Cannabinoid Receptors
THCA interacts with cannabinoid receptors in a way that’s different from THC. THC binds strongly to CB1 and CB2 receptors. But THCA doesn’t attach as well.
Instead, THCA might affect the ECS in other ways. It could increase our body’s own endocannabinoids or change their levels. This unique interaction might explain why THCA offers benefits without making us feel intoxicated.
Studies show that THCA could have anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects. It might help with chronic pain and nausea. Scientists are still learning how THCA works in the body. But its interaction with the ECS seems to be key to its potential benefits.
Effects of THCA on the Body
THCA is getting more attention in medicine for its possible benefits. This non-psychoactive part of raw cannabis has many advantages. It doesn’t make you high like THC does.
Potential Therapeutic Benefits
Studies show THCA might help with inflammation, which could be good for arthritis. It could also protect the brain, helping with Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s. Plus, it might ease nausea, loss of appetite, and epilepsy symptoms.
Interaction with Other Cannabinoids
THCA doesn’t act like THC on cannabinoid receptors. It works differently to create its effects. It’s thought to boost the entourage effect, making cannabis more effective when combined with other compounds.
But, heating THCA turns it into THC. This might not be what everyone wants, especially for those looking for non-psychoactive effects. As research goes on, we’re discovering more about THCA’s unique benefits and how to use them for health.
THCA and Inflammation
THCA, found in raw cannabis, might help fight inflammation. It’s a non-psychoactive compound that could offer benefits without the high THC causes. Let’s look into how THCA could act as an anti-inflammatory and what studies say about its effectiveness.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties
THCA’s anti-inflammatory effects are getting noticed by doctors. Unlike THC, THCA doesn’t need heat to work. It might help with arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease by reducing body inflammation.
THCA interacts with our endocannabinoid system. This could influence our immune responses and inflammation processes.
Studies Supporting THCA’s Role
Early studies on THCA show promising results. Research indicates THCA might protect nerve cells and help with nausea. Some studies suggest it could slow cancer cell growth.
More research is needed, but these findings are encouraging. Scientists are looking into THCA for chronic pain, autoimmune disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases.
People can get THCA from raw cannabis products like juices or salads. This way, they can enjoy its potential benefits without feeling high. As research goes on, we might find more ways THCA can help with inflammation-related health issues.
THCA as a Neuroprotectant
THCA is getting a lot of attention from scientists. It’s found in raw cannabis and might protect our brain health. Let’s look into how THCA could safeguard our neurons and what research says about it.
Mechanisms of Neuroprotection
THCA has special ways to protect our brain cells. It reduces inflammation and acts as an antioxidant. These actions help prevent damage to nerve cells, which could slow brain-related issues.
Its interaction with our body’s systems might explain its protective effects.
Research Findings
Studies on THCA and brain diseases are showing promising results. A 2017 study found THCA has strong neuroprotective activity. This means it could help with Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s.
More human trials are needed, but these early findings are hopeful. They offer natural ways to support brain health.
THCA’s benefits might not stop at protecting neurons. It could also boost our thinking and memory. As research goes on, we learn more about its benefits for our brains and overall health.
Consumption Methods for THCA
THCA consumption methods offer unique ways to experience this non-psychoactive cannabinoid. Let’s explore some popular options for enjoying THCA products and their potential benefits.
Raw Cannabis and Juicing
Raw cannabis is a prime source of THCA. By consuming fresh cannabis leaves or buds, you can get THCA without the high. Juicing raw cannabis is gaining popularity as a THCA consumption method.
It’s simple – blend cannabis leaves with fruits or veggies for a nutrient-rich drink. This approach preserves THCA in its natural form. It allows you to enjoy its potential health benefits without intoxication.
Edibles and Tinctures
THCA products come in various forms, including edibles and tinctures. These offer precise dosing and convenience. THCA edibles might include raw cannabis-infused smoothies or unheated treats.
Tinctures provide a liquid form of THCA that you can add to foods or drinks. Remember, heating these products can convert THCA to THC, changing their effects.
When exploring THCA consumption methods, it’s crucial to choose high-quality THCA products. Whether you opt for raw cannabis or prepared items, always consult with a healthcare professional before adding THCA to your wellness routine.
Legal Status of THCA in the United States
The legality of THCA in the United States is complex. THCA, or tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, is found in raw cannabis plants. It’s not psychoactive. Its legal status depends on federal and state laws about cannabis and hemp.
Federal Regulations
THCA is regulated by the Controlled Substances Act (CSA). The CSA lists tetrahydrocannabinols, including THCA, as Schedule I substances. Hemp products must have less than 0.3% THC to be legal federally. This rule also applies to THC from THCA conversion.
State Laws Overview
State laws on THCA vary a lot. Some states allow cannabis for medical or recreational use. Others have strict bans. In legal states, THCA products might be available. But in strict states, they could be illegal or in a gray area.
The legal situation for THCA is changing. The House Committee on Agriculture wants to ban intoxicating hemp products. This could change THCA’s legal status. The DEA is also looking at cannabis classification under the CSA. These actions could affect THCA’s legal future.
THCA vs. CBD: A Comparative Analysis
Cannabis plants have many compounds, with THCA and CBD being two non-psychoactive ones. A comparison shows they have different properties and benefits. Let’s look at what makes them similar and different.
Similarities and Differences
THCA and CBD have some things in common. They are found in raw cannabis and hemp, and neither gets you high. CBD works with the body’s endocannabinoid system, but THCA’s effects are still being studied.
A big difference is in stability. CBD stays the same over time. But THCA can turn into THC when it’s exposed to heat, light, or air.
Benefits of Each Compound
CBD is popular for its possible health benefits. It’s known to help with anxiety and pain. The World Health Organization says CBD doesn’t have psychoactive effects.
THCA might help with inflammation and protect the brain. It could also be better at stopping nausea than CBD. Both are being looked at for treating seizures and inflammation, but in different ways.
When picking between THCA and CBD products, think about what you need. CBD is easy to find in things like tinctures and edibles. THCA is in raw cannabis flower and concentrates. But remember, THCA can become psychoactive THC when heated. Always talk to a doctor before using cannabis for health reasons.
Side Effects and Safety Profile of THCA
THCA is known for its health benefits without the high of THC. It’s important to know about THCA’s safety and side effects. Most people find it safe, but it’s good to be aware of possible issues.
Known Side Effects
THCA doesn’t make you high, but it might cause some discomfort. You might feel nausea, stomach upset, or skin issues like itching or rashes. These problems are usually mild and happen at high doses.
When THCA is heated, it turns into THC. This can make you feel different and might cause anxiety. It’s key to be careful with how you use it.
Considerations for Use
Start with small amounts of THCA to see how you react. Avoid heating it too much, as it can turn into THC. Choose products from trusted brands that test their products.
THCA might affect how some medicines work. Always talk to a doctor before trying it, especially if you have health issues. Remember, THCA can show up on drug tests if it’s converted to THC. This is important to know for work or legal reasons.
Current Research on THCA
Research on THCA has grown a lot in recent years. Scientists are looking into its possible uses in medicine. Studies have shown that THCA could be very helpful, leading to new ways to use cannabis.
Recent Studies
Recent studies have found that THCA can fight inflammation and protect the brain. It has shown to help with arthritis in animal tests. Scientists have also found ways to measure THCA in the body, making research more precise.
Future Directions in Research
Research on THCA is set to get even better. Scientists want to do more tests on people to confirm what they’ve found in animals. They’re looking into how THCA can help with pain, nausea, and seizures.
They’re also trying to figure out the best way to use THCA. With most hemp samples showing high levels of THCA, they might work on making products safer and more legal.
As research on THCA goes on, we might find even more ways it can help. This could lead to better treatments and care for patients. The future of studying THCA looks very promising.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding THCA
As we conclude our exploration of THCA, it’s evident that this non-psychoactive cannabinoid has great promise. With over 100 cannabinoids in the cannabis plant, THCA is unique. It has properties and benefits that set it apart.
Summary of Benefits and Uses
THCA is found in raw and live cannabis plants. It offers many potential health benefits without causing a high. Research shows it might help with inflammation and protect the brain.
Unlike THC, THCA doesn’t bind to cannabinoid receptors. This is why it doesn’t have psychoactive effects.
Encouragement for Further Research
Though early studies on THCA are promising, more research is needed. The cannabis industry is growing fast, with THCA-rich products like tinctures and vape cartridges becoming more common. As we move forward, studying THCA could reveal more health benefits.
The future of THCA looks bright. With ongoing research, we might find even more ways it can help our health and well-being.