Ever wondered if that raw cannabis leaf could get you high? You’re not alone. The buzz around THCA has left many scratching their heads. Is it a loophole to legal highs, or just another overhyped trend? Let’s dive into the world of THCA and uncover the truth about its effects.
THCA, or tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, is the talk of the town in cannabis circles. It’s abundant in raw cannabis plants but doesn’t pack the punch you might expect. Unlike its famous cousin THC, THCA won’t send you on a psychedelic journey – at least not in its natural state.
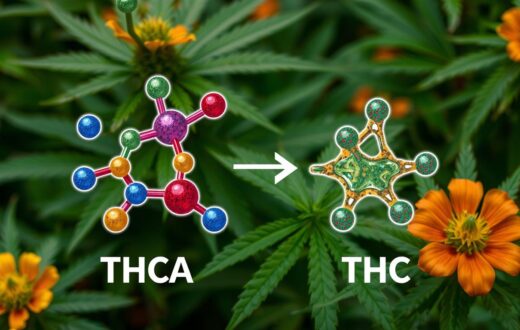
But here’s where it gets interesting: THCA is like THC’s shy sibling. It’s not psychoactive on its own, but with a little heat, it transforms into the THC we all know. This process, called decarboxylation, is the key to unlocking THCA’s hidden potential.
As we explore the ins and outs of THCA, we’ll uncover its legal status, potential benefits, and why it’s causing such a stir. Whether you’re a curious newcomer or a seasoned cannabis enthusiast, there’s plenty to learn about this fascinating compound. Ready to separate fact from fiction? Let’s get started!
Understanding THCA: The Basics
THCA stands for tetrahydrocannabinolic acid. It’s a key compound found in raw cannabis plants. This compound is vital for the plant’s healing powers and can make up to 90% of THC content. Let’s explore what THCA is and how it differs from THC.
What is THCA?
THCA is a non-psychoactive compound found in fresh cannabis buds. It’s the precursor to THC, which causes the “high” from marijuana. Products rich in THCA include raw cannabis, tinctures, and extracts. Some, like THCA crystals, can have up to 98% potency.
How is THCA Different from THC?
THCA and THC have different chemical structures and effects. THCA doesn’t cause a high when consumed raw, unlike THC. When THCA is heated, it turns into THC. This is why smoking or vaping cannabis has psychoactive effects, but eating raw cannabis doesn’t.
It’s important to note that THCA is not as controlled as THC. This is because it has low psychoactive properties. However, legal rules about THCA can vary based on laws in different places.
The Science Behind THCA
THCA is a key part of cannabis. It’s important for the plant’s properties. We’ll look at its chemical structure and how it turns into THC, the part that gets you “high” from cannabis.
Chemical Structure of THCA
THCA has a special structure. It’s different from THC because of a carboxylic acid group. This group is why THCA is not psychoactive and why raw cannabis doesn’t get you high.
Conversion of THCA to THC
Turning THCA into THC is called decarboxylation. This happens when cannabis gets hot or ages. When this happens, THCA loses its acid group and becomes THC.
Methods for extracting THCA try to keep it in its original form. Not all THCA turns into THC. About 88% does, but factors like temperature and storage can change this.
Knowing this science is key for both fun users and those looking at cannabis health benefits. It shows why eating raw cannabis doesn’t get you high, but smoking or baking it does. This knowledge helps unlock cannabis’s full potential.
Psychoactivity Explained
Psychoactivity is about how substances change brain function. It can alter how we see things, feel, and act. Knowing about psychoactive effects helps us understand how substances affect us.
What Does Psychoactive Mean?
Psychoactive substances change brain chemistry. This leads to changes in how we think, feel, or behave. For instance, THC in cannabis makes us feel happy and changes how we see time and feel things.
Common Psychoactive Substances
Many things we use daily have psychoactive effects. Caffeine in coffee wakes us up, while alcohol relaxes us. Nicotine in cigarettes gives a quick high. In cannabis, THC is the main psychoactive compound, causing the “high” feeling.
THCA, found in raw cannabis, isn’t psychoactive. But when heated, it turns into THC. This is why eating raw cannabis doesn’t have the same effect as smoking or vaping it.
Studies show about 30% of regular cannabis users might develop a use disorder. Long-term THC use can lead to depression and breathing problems. It’s important to know these risks before using cannabis. Always talk to a healthcare professional for advice.
THCA and Psychoactivity
THCA is found in raw cannabis plants and is different from THC. The relationship between THCA and psychoactivity is complex and often misunderstood. Let’s explore the truth about THCA effects and how they compare to THC.
Is THCA Psychoactive?
THCA itself is not psychoactive when consumed raw. Unlike THC, it won’t produce the euphoric high associated with marijuana use. This key difference stems from THCA’s molecular structure, which prevents it from binding effectively to cannabinoid receptors in the brain.
THCA potency in raw cannabis doesn’t translate to intoxicating effects. This makes it an appealing option for those seeking potential benefits without impairment.
Factors Influencing THCA’s Effects
While THCA doesn’t cause a high, it may offer therapeutic benefits. Research suggests THCA could have anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties. The most significant factor influencing THCA’s effects is heat exposure.
When heated to around 220-245°F, THCA converts to THC through a process called decarboxylation. This transformation occurs when smoking, vaping, or cooking cannabis, potentially leading to psychoactive effects. THCA potency in raw plants can vary, affecting the strength of both therapeutic and psychoactive effects after heating.
Users interested in THCA’s potential benefits without psychoactivity should explore raw cannabis juicing, tinctures, or topicals.
The Role of Heat in THCA
Heat is key in changing THCA into THC, the part that makes cannabis psychoactive. This change, called thca decarboxylation, is essential for cannabis’s full effect.
Decarboxylation: The Process
When THCA loses its carboxyl group due to heat, it turns into THC. This change starts at 220°F (104°C). The best conversion happens around 300°F (149°C). But, going over 400°F (204°C) can harm THC’s strength.
How Cooking Affects THCA
Cooking cannabis-infused foods starts the thca conversion. The speed of this change depends on the temperature and how long it cooks. Lower heat needs longer cooking to fully convert THCA.
Even room temperature can slowly change THCA over time. This is why keeping cannabis products in the right place is important to keep their strength.
For those using medical marijuana, getting THC right is crucial. It makes the medicine work well. If it’s not done right, the medicine might not work as well. Ways to convert THCA include smoking, vaporizing, baking, and using a slow cooker.
Medical Uses of THCA
THCA is a non-psychoactive compound found in raw cannabis. It’s getting attention for its health benefits. This cannabinoid works with the body’s receptors in special ways. It offers promising effects without the high of THC.
Potential Health Benefits
Research on THCA shows it could have many medical uses. It might help with arthritis and autoimmune disorders because of its anti-inflammatory properties. THCA could also protect the brain and help with neurological issues.
For those going through chemotherapy, THCA might reduce nausea. This is because of its anti-emetic properties.
Research on THCA and Conditions
Studies on THCA are still going on. Early results suggest it could help with chronic pain and diseases that harm the brain. A study in the British Journal of Pharmacology found THCA has anti-inflammatory effects in mice.
It’s also popular in alternative medicine for its antioxidant properties. While more research is needed, THCA might help with Alzheimer’s, epilepsy, and multiple sclerosis.
As research on THCA continues, we learn more about its benefits. It’s important to note that THCA is best consumed raw to keep its special properties. Users should be aware of possible mild side effects. Also, check local laws, as THCA’s legal status varies.
The Legal Status of THCA
Understanding the legal status of THCA can be confusing. The U.S. Drug Enforcement Agency lists tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) as a Schedule I controlled substance. But, the 2018 Farm Bill created a gray area. THCA from hemp with no more than 0.3% THC isn’t controlled under the Controlled Substances Act.
THCA vs. THC: Legal Distinctions
THCA and THC have different legal statuses. Raw THCA is promising for health benefits without causing a high. It’s not intoxicating until it’s heated.
This process, called decarboxylation, turns THCA into THC. Once this happens, it falls under stricter THC regulations.
Regulations in Different States
Thca regulations vary across states. Some allow its use, while others don’t. The federal government is reviewing cannabis classification.
They might move it from Schedule I to Schedule III. This could relax rules on adult-use cannabis nationwide. The hemp industry faces uncertainty with upcoming Farm Bill changes.
Proposed amendments could impact THCA products and small hemp producers. Keep an eye on your local laws as they may change.
Consumer Products Containing THCA
THCA products are becoming more popular among cannabis fans. They offer special benefits without the high of THC. Let’s look at some common THCA-rich items available to consumers.
THCA-Rich Strains of Cannabis
THCA flower comes from strains grown to have lots of THCA and little THC. Strains like Gorilla Glue #4, Sour Diesel, and Wedding Cake are very potent. These strains must have less than 0.3% THC to be sold legally.
Quality THCA flower is judged by its look, smell, feel, and cannabinoid content.
Edibles and Tinctures
THCA consumption isn’t just about smoking. Edibles and tinctures are great alternatives. Some people add THCA flower to smoothies or juice it for a raw cannabis experience. Tinctures offer a concentrated THCA for easy dosing.
These products aim to keep THCA’s potential health benefits, like reducing inflammation.
The THCA market is growing fast, with brands like Diamond CBD and Cannaflower leading. As research continues, we’ll see more innovative THCA products. But, remember, laws about THCA vary by state, so check local rules before buying.
THCA’s Safety Profile
THCA safety is a big deal for cannabis users. Unlike THC, THCA doesn’t get you high when it’s raw. But, it’s not completely side effect-free.
Side Effects of THCA
THCA side effects are usually mild. Some people feel sleepy or tired after using it. These feelings last a few hours.
Another common side effect is dry mouth, or “cottonmouth.” This happens because THCA can lower saliva production. Drinking water or chewing sugar-free gum can help.
THCA vs THC: A Safety Comparison
THCA is safer than THC in many ways. It doesn’t cause the same cognitive problems as THC. This means no memory loss or anxiety.
But, THCA can lower blood pressure. This might cause dizziness or lightheadedness in some. Long-term use might affect brain function, but more research is needed.
Smoking THCA-rich products can harm your lungs. Try vaping or edibles instead. If you’re pregnant, elderly, or have health issues, talk to a doctor first. Start with small amounts and watch how your body reacts.
Public Perception of THCA
As cannabis becomes more mainstream, public views on THCA are changing. More people are learning about THCA, but myths still exist. Many confuse THCA with THC, not understanding their differences.
Common Misunderstandings
One big myth is that all THCA products cause a high. This comes from not knowing about decarboxylation. THCA is non-psychoactive in its raw form. It turns into THC, the compound that causes a high, when heated.
Legal gray areas add to the confusion. While THC is often illegal, THCA is typically legal to use and possess.
Rising Consumer Interest
Despite these mix-ups, interest in THCA is on the rise. People are attracted to its health benefits without the high. THCA products come in various forms like flower, vapes, and live resin gummies.
Some products, like THCA diamonds, can contain up to 99% THCA. This variety shows the growing market for THCA.
As interest grows, so does the need for solid cannabis education. Clear info helps people make smart choices about using THCA. It’s important to know that THCA can stay in your system – up to 4 days in urine and 90 days in hair.
With more research and education, public understanding of THCA will likely improve over time.
Future of THCA Research
The cannabis world is changing fast, with THCA research leading the way. As we learn more about this compound, we open up new areas for science and law.
Areas for Further Study
THCA research is just starting, but it’s full of promise. Scientists want to know more about its healing powers, like fighting inflammation and protecting the brain. In 2023, THCA sales made up 7.3% of the $2.8 billion hemp market. This interest means we need more studies on people to back up animal research.
Potential Impacts on Cannabis Laws
As we learn more about THCA, it could change cannabis laws. Right now, laws focus on THC levels, with hemp allowed to have less than 0.3% delta-9 THC. But THCA’s special qualities might lead to new, more detailed laws. For example, some places let THCA flower be sold as hemp, even if it can turn into THC when heated.
This situation shows we need updated laws based on new research. The future of THCA research looks bright for medical breakthroughs and legal changes. As we discover more about this compound, we might see laws that are more based on science.
Tips for Using THCA
Exploring thca products is exciting for cannabis fans. Whether you’re new or want to improve your experience, we’ve got tips for you.
How to Enjoy THCA Products
Raw cannabis juicing is a favorite for thca fans. It lets you enjoy THCA’s benefits without THC’s high. THCA-rich edibles are also great. But, remember, heat turns THCA into THC, so don’t cook or heat these products.
Considerations for New Users
Start with small doses if you’re new to thca. Gradually increase as you see fit. This helps you find the right amount without side effects.
Buying thca products from trusted sources is key for quality and purity. Also, know that THCA can show up on drug tests if it turns into THC. So, be careful if you’re tested.
THCA might help with inflammation and protect brain cells, research says. But, always talk to a doctor before using it for health reasons or with other meds. They can give advice tailored to your health and help you use THCA safely.
Conclusion: THCA and Psychoactivity
As we conclude our look at THCA, it’s clear it has a special place in the world of cannabinoids. Found in raw cannabis plants, THCA is different from THC. While THC is known for its psychoactive effects, THCA stays non-psychoactive on its own.
Recap of Key Points
THCA’s transformation into THC through heat is key to understanding its effects. This change, caused by heat, makes THCA into the psychoactive THC we know. Even without being psychoactive, THCA shows promise in treating inflammation and protecting the brain.
The Bottom Line on THCA’s Effects
THCA’s effects are quite different from THC’s. THC can make you feel euphoric and relaxed but can also cause dry mouth and memory issues. THCA, however, doesn’t have these effects unless it’s heated. This makes THCA appealing for those looking for cannabis benefits without the high. As research on THCA grows, it could change how we see cannabis in medicine and fun.