Could THCA be the key to unlocking new medical breakthroughs? Recent research is shedding light on this non-psychoactive cannabinoid. It’s sparking excitement in the scientific community.
A groundbreaking study was published in the Journal of Cannabis Research in 2024. It has gotten over 800 accesses since its release. This research looks into the details of cannabinoid analysis in Hemp Cheungsam, a non-drug type of Cannabis sativa.
Scientists used advanced phytochemical profiling techniques to find interesting insights into THCA biosynthesis. They found that Hemp Cheungsam mainly expresses cannabinoid biosynthesis genes in its flowers. CBDA synthase was found to have higher expression than THCA and CBCA synthase.
This research not only deepens our understanding of THCA but also opens doors for future studies on its potential therapeutic uses. As we continue to explore the complexities of cannabis, THCA is a promising area for ongoing scientific research.
What is THCA and Its Significance?
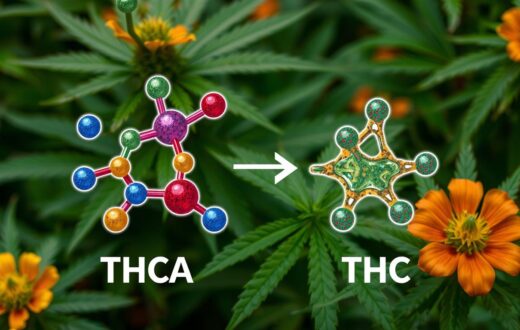
THCA stands for tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, a key compound in raw cannabis plants. It’s found in fresh buds and is important in cannabis testing. Unlike THC, THCA doesn’t cause psychoactive effects when raw.
This unique property has caught the attention of the medical world and the cannabis industry. It’s a reason for much interest.
Chemical Composition of THCA
THCA has a similar structure to THC but has a carboxylic acid group. This difference is key. It prevents THCA from binding to brain receptors like THC does.
Cannabis testing labs look at THCA levels in plants. This is because THCA turns into THC when heated, which can cause intoxication.
How THCA Differs from THC
The main difference between THCA and THC is their effects on the body. THC is known for its psychoactive effects, but THCA is not intoxicating when raw. This is important for medical research and legal reasons.
In 2022, a report found 49 out of 53 hemp samples had more THCA than allowed. Terpene identification helps tell these compounds apart and their effects.
Research shows THCA might have health benefits, like reducing inflammation and protecting the brain. It might even help with cognitive issues, like Alzheimer’s. But, most studies are on animals, so more research on humans is needed.
The History of THCA Research
The study of THCA started in the 1970s and 1980s. Scientists first looked into cannabinoids back then. THCA was not well-known at first but became more interesting as research deepened.
Early studies focused on its chemical makeup and how it relates to THC.
Early Studies and Discoveries
In the early 2000s, THCA research really took off. Scientists found out THCA is very common in cannabis. It comes from CBGA, a key part of hemp.
This discovery made people want to learn more about how to extract and study THCA.
Developments in Cannabis Science
As cannabis science grew, researchers looked into THCA’s health benefits. A 2017 study showed THCA is very good at protecting the brain. Another study found it helps reduce nausea in rats, even at lower doses than THC.
These findings led to more research into THCA’s anti-inflammatory and brain-protective effects.
Now, thanks to new hemp growing methods, it’s legal to extract THCA from hemp. This has opened up new research paths and medical uses. As more places legalize cannabis, the need for more research into cannabinoids, including THCA, is growing.
Current Trends in THCA Research
Research on THCA is growing fast in the medical cannabis world. This non-psychoactive part of raw cannabis plants is catching the eye of scientists and health experts. It’s because THCA might help with health issues without causing a high like THC.
Focus Areas for Researchers
Scientists are diving into THCA’s anti-inflammatory effects and how it works with our body’s endocannabinoid system. They think THCA might protect the brain, leading to new treatments. They’re also looking into its impact on cancer cells, but the findings are still unclear.
Popularity in Medical Studies
THCA is now a big deal in medical studies because of its special traits. It doesn’t get you high, making it great for treatments where strict rules apply. Researchers are studying its effects on nausea, appetite, and muscle spasms, similar to THC but without the psychoactive effects.
The cannabis industry is seeing more THCA products, especially in wellness. Sublingual THCA drops are popular for their quick absorption and lack of high. THCA flower, with lots of THCA and little THC, is a legal choice in places with strict THC laws. These trends show how research is guiding the future of medical cannabis and shaping new products within legal bounds.
Therapeutic Potential of THCA
THCA, the non-psychoactive precursor to THC, has shown great promise. Researchers are studying its benefits through cannabinoid analysis. This compound, found in raw cannabis, offers health advantages without the “high” of THC.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Studies show THCA’s strong anti-inflammatory effects. It could help those with arthritis and Crohn’s disease. Its ability to reduce inflammation might lead to new treatments for these chronic conditions.
Neuroprotective Effects
THCA may protect the brain from harm. Research suggests it could fight neurodegenerative diseases. This could lead to new therapies for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s patients.
Possible Anti-Cancer Benefits
Early research suggests THCA might slow cancer cell growth. While more studies are needed, this finding excites scientists. Phytochemical profiling helps identify these potential benefits. THCA also seems to ease nausea in chemotherapy patients and boost appetite.
THCA’s therapeutic potential extends beyond these areas. It may help with pain relief and muscle spasms, benefiting conditions like multiple sclerosis. As research progresses, we may uncover even more ways THCA can improve health and wellbeing.
THCA vs. THC: Understanding the Differences
Cannabis testing shows big differences between THCA and THC. THCA is the first form of THC and has a special structure. This makes it work differently in our bodies and its legal status.
Psychoactive Properties
THCA doesn’t get you high until it turns into THC with heat. Raw THCA can still help without the psychoactive effects. On the other hand, THC can make you feel different, like having red eyes and wanting to eat more. The effects of THC start 15 to 90 minutes after you use it.
Legal Status in the U.S.
The laws about THCA and THC are complicated. THC is still illegal at the federal level, but many states allow it for medical use. THCA’s legal status is not as clear, depending on if it can turn into THC. This makes it important to keep testing and updating the laws.
Medical Applications
Research on medical cannabis looks at both THCA and THC for different health issues. THC might help with chronic pain and make food taste better for people getting chemotherapy. THCA, though less studied, could also help without making you feel high. As we learn more, testing cannabis will be key to understanding its health benefits.
Clinical Trials Involving THCA
Research on THCA in medical cannabis is growing. Scientists are looking into its benefits. They found that THCA, found in raw cannabis, has promising uses.
Recent Completed Studies
A study on mice showed THCA’s potential in fighting Alzheimer’s disease. It improved their cognitive skills. This finding could lead to new treatments for neurological issues.
Ongoing Research Projects
Now, scientists are studying THCA in many areas. They’re looking into its effects on metabolic syndrome and weight loss. They’re also exploring its use as an antiemetic agent. These studies aim to learn more about THCA’s benefits.
Even though the research is promising, more human trials are needed. These studies will help us understand THCA’s full potential and safety. As research in medical cannabis grows, THCA remains a key area of interest.
The Role of THCA in the Cannabis Plant
THCA is crucial in cannabis plants. It’s the precursor to THC, the psychoactive part we know. Plants make THCA naturally, which turns into THC when heated.
Knowing about THCA is important for hemp growers and those who study plant chemicals.
THCA Biosynthesis
THCA is made in the trichomes of cannabis plants. These tiny structures on the plant’s surface are where cannabinoids are made. As the plant grows, it makes THCA instead of THC right away.
Factors Affecting THCA Levels
Many things can change how much THCA is in cannabis plants. Genetics are a big factor, with some strains making more THCA than others. Growing conditions like light, temperature, and soil also matter.
When to harvest is key too. Plants picked later often have more THCA. Storing plants properly after harvest helps keep THCA levels up.
For hemp growers, managing these factors is key to getting the right chemical makeup.
Phytochemical profiling is a great way to check THCA levels. It helps growers and researchers understand the plant’s chemical makeup. It’s especially useful in hemp cultivation, where keeping THC levels low is important.
By watching THCA levels, growers can better control the THC in their products.
THCA Extraction Methods
THCA extraction uses different techniques to get this valuable compound from cannabis plants. Each method has its own benefits and challenges. These affect the quality of the final product and its uses in cannabis products.
Common Techniques in Use
Solvent-based extraction is common in the industry. Ethanol extraction is known for its efficiency and safety. CO2 supercritical extraction allows for precise control. Butane Hash Oil (BHO) extraction makes strong concentrates like shatter and wax.
Ice water hash extraction is a solvent-free option, prized for its purity. Dry sift and rosin pressing are gaining popularity. They capture the plant’s essence without chemicals.
Pros and Cons of Extraction Methods
Solvent-based methods like CO2 and ethanol are good for big production but might leave residues. Mechanical methods like dry sift are safer but less efficient. Rosin pressing is a good mix of quality and simplicity.
Each method affects the final product in different ways. For example, live resin extraction keeps high terpene content. THCa crystallization can get up to 99% purity. Testing cannabis is key to ensure safety and potency, no matter the method.
The Future of THCA Research
THCA research is growing fast, opening new areas in medical cannabis. As we learn more about this compound, new technologies are changing how we understand and use it.
Emerging Technologies
New analytical tools are making it easier to study cannabinoids. These tools help researchers look at THCA in new ways, leading to better medical treatments. Nanotechnology is also being explored, which could make THCA treatments more effective for different health problems.
Potential New Applications
THCA research is looking bright. Scientists are looking into personalized medicine based on each person’s endocannabinoid system. This could mean treatments made just for you. They’re also working on new ways to extract THCA, making it purer.
Legal issues are also affecting THCA research. The 2024 Farm Bill changed what counts as hemp, including THC levels. This might limit the use of high-THCA products. But, despite these hurdles, research on THCA keeps moving forward. It’s driven by its potential health benefits and the fact it doesn’t get you high.
Public Perception of THCA
Many people don’t know much about THCA, a part of cannabis. As medical cannabis becomes more popular, learning about THCA is key. But, there’s still a lot of confusion.
Many think THCA is the same as THC, but they’re not the same. This confusion comes from not understanding cannabis well.
Awareness and Misconceptions
Some believe THCA makes you high like THC. But, THCA doesn’t have this effect. This confusion comes from not knowing about cannabis compounds well.
Some also think THCA is illegal, but its legal status is different from THC. The amount of THCA in plants can change, affecting how strong it is.
Education and Outreach Efforts
Cannabis companies and researchers are working to clear up these myths. They’re launching campaigns to teach people about THCA. They want to explain its benefits and legal status.
Medical cannabis experts are also playing a big role. They help patients understand how THCA is different from THC. This is important for its use in medicine.
As research goes on, how people see THCA will likely change. It’s important to share clear, easy-to-understand information. This way, myths can be debunked, and people can see THCA in a new light, different from THC.
THCA and the Endocannabinoid System
The endocannabinoid system is vital for our body’s functions. THCA, found in raw cannabis, interacts with it in special ways. Knowing these interactions helps us understand medical cannabis better.
Interaction with Cannabinoid Receptors
Unlike THC, THCA doesn’t strongly bind to CB1 receptors in the brain. This is why it doesn’t make you feel “high.” Instead, it might affect CB2 receptors all over the body. This could be why THCA is seen as promising for health benefits.
Implications for Health
THCA’s unique traits make it a focus in medical cannabis research. It might offer relief without the psychoactive effects. Studies hint at its potential to reduce inflammation, nausea, and even slow cancer cell growth.
To enjoy these benefits, people can eat raw cannabis or cook it below 220°F. This way, THCA won’t turn into THC. As we delve deeper into THCA and the endocannabinoid system, we find new uses for cannabis in health. This could lead to more precise treatments and a deeper understanding of cannabis’s effects on us.
Legal Considerations Surrounding THCA Research
The legal rules for THCA research in the U.S. are complex and keep changing. The 2018 Farm Bill made hemp products with less than 0.3% THC legal. But, THCA’s legal status is still unclear. This makes it hard to follow the rules and do research on THCA.
Regulations in the United States
In November 2023, President Biden extended the 2018 Farm Bill until September 30, 2024. This law protects hemp products with less than 0.3% THC under federal law. But, each state has its own cannabis laws.
For example, California’s AB 45 limits hemp products to 0.3% total THC. Florida is thinking about limiting delta-9 THC in hemp products to 2mg per serving.
Impacts on Research Funding
The unclear legal status of THCA makes it hard to get funding for research. Researchers struggle to get legal THCA samples and find funding. The DEA’s new rule that THCA should be counted in total THC adds more complexity.
This rule could make many hemp products illegal. It might limit research opportunities. Despite these challenges, THCA research is still growing. Healthcare professionals are interested in THCA’s health benefits, which drives the need for more studies.
As laws change, researchers must follow the rules while continuing important THCA research.
Market Demand for THCA Products
The demand for THCA products is growing fast. This is because more people want non-psychoactive cannabinoids. Hemp farming and extraction are key to meeting this need.
Consumer Trends
THCA products are becoming more popular. People are looking for alternatives to regular cannabis. These products must have less than 0.3% delta-9 THC, as set by the 2018 Farm Bill.
This rule has made a special market for these products. It attracts both long-time cannabis users and newcomers.
Industry Growth and Forecast
The THCA market is looking up. In early 2024, the prices for THCA flower were as high as or higher than cannabis flower in some states. Indoor THCA flower prices dropped by 7%, while greenhouse-grown flower prices fell by 11% per pound.
Despite some hurdles, the THCA industry is moving forward. Small hemp businesses are adjusting to the market. Some states are still figuring out how to regulate THCA products.
As the industry grows, we’ll see more improvements in hemp farming and extraction. This will help meet the increasing demand for THCA products.
Conclusion: The Path Forward for THCA Research
THCA research has made great strides, showing its potential in medical cannabis. This non-psychoactive compound is exciting because it offers benefits without the psychoactive effects of THC.
Key Takeaways
THCA’s journey from raw cannabis to a potential therapeutic is captivating. Its non-psychoactive nature and benefits make it a focus in medical cannabis. The process of converting THCA to THC at 115℃ shows the balance between these compounds.
Future Directions for Study
The future of THCA research looks promising but challenging. We need more human trials to understand its benefits for conditions like arthritis and lupus. As laws change, we’ll learn more about THCA’s uses. The rise in THCA products shows growing interest and potential for discovery.